Free Download Samsung Galaxy Ace GT-S5830 VIR United kingdom 2.3.5 Gignerbread S5830XWKS3
Wireless Device
..:: Alcatel BB Multi Unlocker Key v15.0 Clanecuador ::..
Go to link download
Go to link download

Go to link download
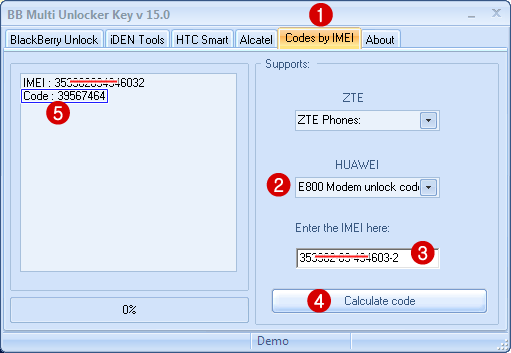
Configuration Internet Connection There are several possibilities to enter the unlock code obtained previously. Download the latest version of the dashboard Mobile Partner This connection manager is compatible with all unlocked Huawei modems.


Go to link download
Go to link download
Go to link download


Go to link download

Go to link download
 Huawei E353 WCDMA 3G USB Wireless Modem Dongle
Huawei E353 WCDMA 3G USB Wireless Modem Dongle Download (Télécharger) Firmware Update Huawei E353 | General | |
|---|---|
| Model | E353 |
| Sub-Models | E353s-1, E353Ws, E353Ws-1, E353s-6, E353u-1, E353u-2, E353u-6, E353Wu-1 |
| Brand | HUAWEI |
| Type | 3G USB Modem |
| Ports | USB 2.0 High Speed |
| Modem | |
|---|---|
| Chipset | Qualcomm MSM8200A |
| Firmware | 11.810.09.40.156 |
| Algorithm | NEW ALGO |
| Hardware ver. | CP1E353UM |
| Dimensions | |
|---|---|
| Weight | <26 g |
| Height | 89 mm |
| Width | 27 mm |
| Depth | 12 mm |
| Frequency Bands | |
|---|---|
| 3G: HSPA+/UMTS | 900 MHz, 2100 MHz |
| 2G: GSM/GPRS/EDGE | 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 1900 MHz |
| Connectivity Speed | |
|---|---|
| HSPA+ | 21.6 Mbps |
| HSDPA | 14.4 Mbps |
| HSUPA | 5.76 Mbps |
| UMTS | 384 kbps |
| EDGE | 236.8 kbps |
| GPRS | 57.6 kbps |
| Memory Support | |
|---|---|
| Memory Capacity | 32 GB |
| Memory Card Slot | SD Card |
| System Requirements | |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows 2000 * Windows XP * Windows Vista * Windows 7 & 8 * Mac |
Go to link download
Go to link download

Go to link download

Go to link download
HOW TO HARD RESET BLACKBERRY Z3.
Method to Hard Reset:
Step 1: Remove the battery, and then reinsert it.
Step 2: Press and hold the Power key for 10 seconds.
Step 3: Press and hold the Volume up key and Volume down key at the same time for 10 seconds.
Go to link download
Symphony X120 Official Firmware free Ver-X120_Tinno_E560_MP_BEGNALI_01_08_18.08.2010 Ver-X120_Tinoo_E560_MP_BEGNALI_01_11_22.11.2010 | |
| skhasan2005@yahoo.com | |
Go to link download
 Device Name : Samsung Galaxy Ace 3 LTE South America GT-S7275B
Device Name : Samsung Galaxy Ace 3 LTE South America GT-S7275BGo to link download
Go to link download
 |
| Infinix Hot 3 |
Body | |
| Form factor | Touchscreen |
| Colors | Gray, Gold, Silver, Pink, Blue |
| Cover | Plastic |
Display | |
| Type | Super AMOLED capacitive touchscreen, 16M colors |
| Size | 5.5-inch IPS Touch Display |
| Resolution | 720 X 1280 pixels |
| Pixel Density | 267ppi |
Memory And OS | |
| Card slot | microSD, up to 32 GB |
| Inbuilt | 16GB |
| OS | Android 5.1.1 Lollipop |
| Processors | 1.3GHz quad-core 64-bit CPU, MediaTek Cortex-A53 MT6580 chipset, Mali400-MP2 GPU |
| RAM | 1GB/2GB |
Camera | |
| Primary | 8.MP |
| Features | phase detection, HDR, face and smile detection,autofocus, Geo-tagging camera with LED flash |
| Video | 1080p@30fps |
| Secondary | 2MP, up to 1920 x 1080-pixel pictures, soft flash |
Battery | |
| Capacity | 3000mAh Li-Ion battery |
Connectivity | |
| 3G | Yes |
| 4G | Yes |
| WIFI | Wi-Fi 802.11 a/b/g/n, Wi-Fi hotspot, DLNA, Wi-Fi Direct |
| Bluetooth | Yes v4.2 |
| GPS | A-GPS |
| NFC | No |
| USB | MicroUSB v2.0 |
| SIM | Dual micro SIM |
Other Features | |
| Sensors | Accelerometer, proximity, Ambient light sensor |
Go to link download
Nokia X2-00 RM-618 V 08.35 Bangla mcu ppm cnt RM-618 08.35.mcusw RM-618 08.35.ppm Ms RM-618 08.35.cnt.image Ms | ||||
| Nokia X1-01 RM-713 V. 007.500 Bangla mcu ppm cnt RM-713 007.500.mcusw RM-713 007.50.ppm.ms RM-7130 Nai07.50.cnt.ms Nokia 202 RM-834 V 20.52 Bangla mcu ppm cnt RM-834 20.52.mcusw RM-834 20.52.ppm Bg RM-834 20.52.image.cnt Bg |
Go to link download

Go to link download